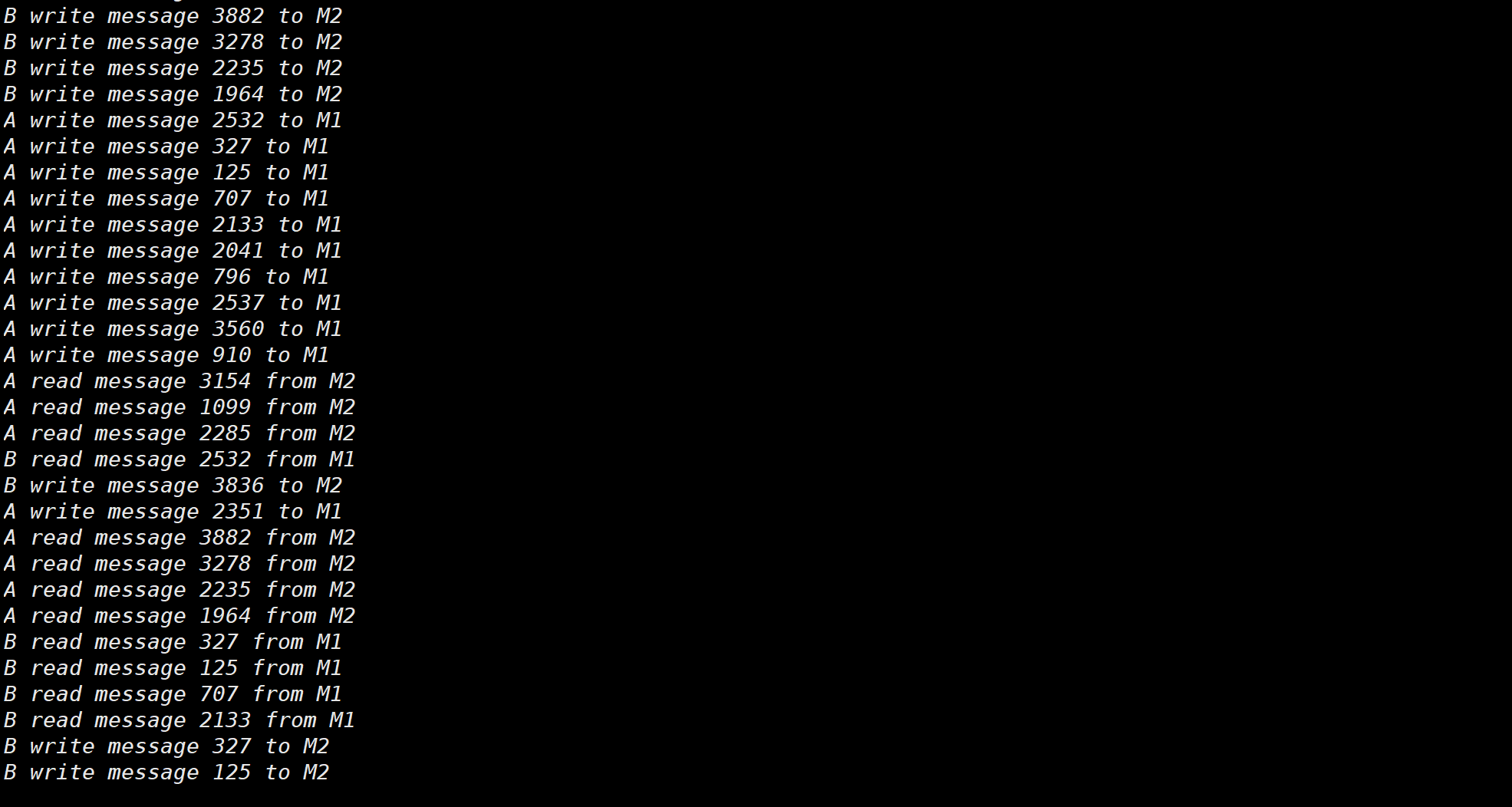# 系统调用与进程通信# 系统调用# 查询 sys_call_table 的地址通过命令:
sudo cat /proc/kallsyms | grep sys_call_table
查找到 sys_call_table 的地址为 0xffffffffb48001e0 :
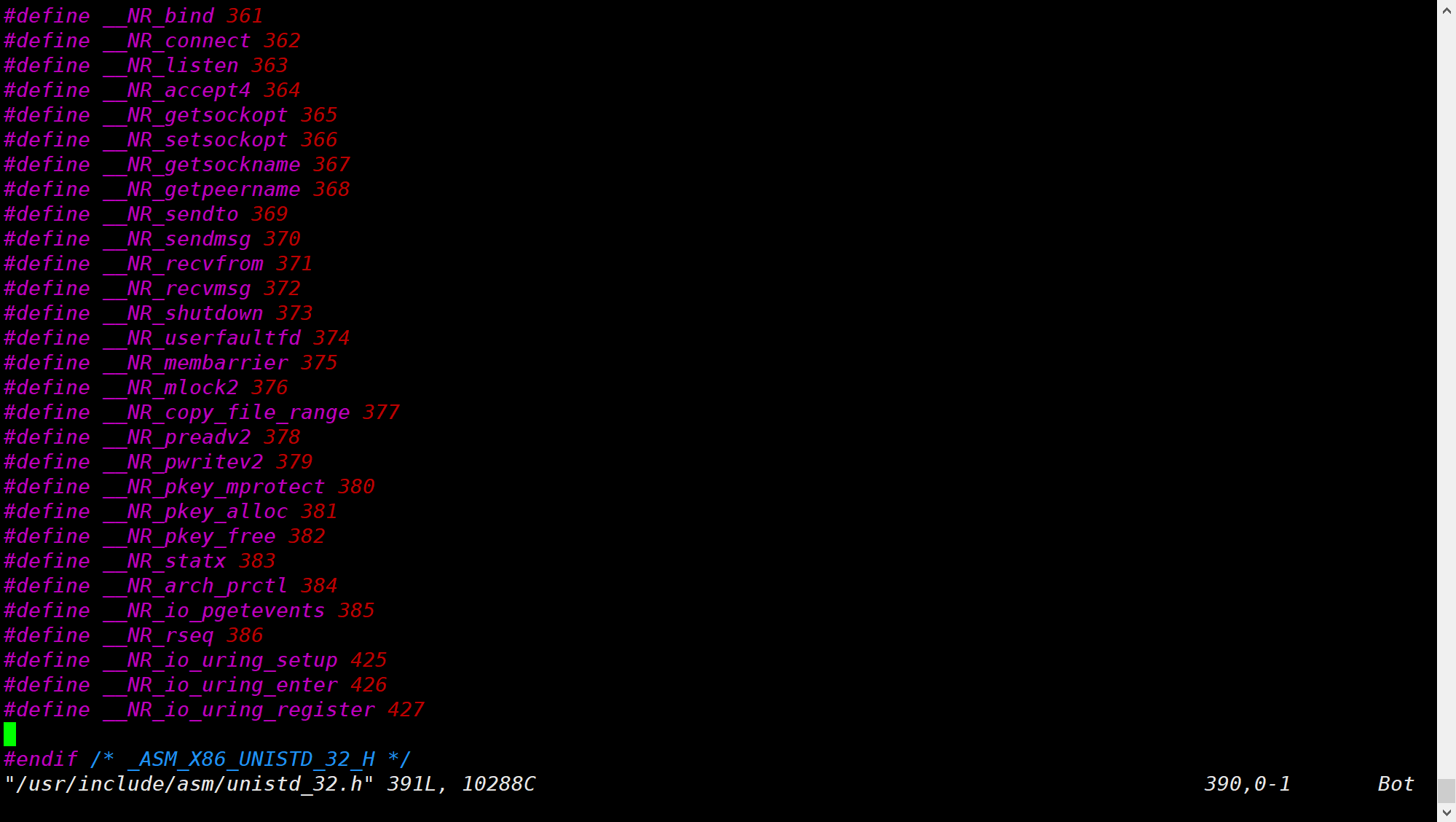
# 查询可用的系统调用号通过命令打开 unistd_32.h :
vim /usr/include/asm/unistd_32.h
如图所示,可以看到 387 号 是可用的系统调用号:
# 创建 dzc_test.c 文件创建 dzc_test.c 文件,在文件内定义系统调用,其中使用到的 sys_call_table 地址和可用系统调用号为上述的 0xffffffffb48001e0 以及 387
代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/unistd.h> #include <linux/sched.h> "Dual BSD/GPL" );#define SYS_CALL_TABLE_ADDRESS 0xffffffffb48001e0 #define NUM 387 int orig_cr0; unsigned long *sys_call_table_my=0 ;static int (*anything_saved) (void ) ; static int clear_cr0 (void ) unsigned int cr0=0 ;unsigned int ret;asm volatile ("movq %%cr0,%%rax" :"=a" (cr0)) ;0xfffffffffffeffff ;asm volatile ("movq %%rax,%%cr0" ::"a" (cr0)) ;return ret;static void setback_cr0 (int val) asm volatile ("movq %%rax,%%cr0" ::"a" (val)) ;long sys_mycall (void ) "20192121026_邓智超\n" );return current->pid; static int __init call_init (void ) unsigned long *)(SYS_CALL_TABLE_ADDRESS);"开始执行系统调用\n" );int (*)(void ))(sys_call_table_my[NUM]);unsigned long ) &sys_mycall;return 0 ;static void __exit call_exit (void ) "系统调用结束\n" );unsigned long )anything_saved;
# 创建 Makefile 文件查询到内核源码的路径为 **/usr/src/kernels/4.18.0-193.14.2.el8_2.x86_64**
使用 vim Makefile 命令创建 Makefile 文件,并在其中添加内容为:
obj-m:=dzc_test.o
# 安装内核模块执行命令 make ,并通过命令 **ls | grep ‘dzc_test.*’** 查看是否执行成功
使用如下命令插入模块:
使用如下命令检查插入是否成功:
可以看到名为 dzc_test 的模块,说明插入成功。
# 测试创建 test.c 并在其中添加代码:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <sys/syscall.h> #include <unistd.h> int main () unsigned long x = 0 ;387 ); printf ("20192121026_邓智超:%d\n" , x);return 0 ;
使用 gcc test.c 和 ./a.out 命名查看运行结果:
通过 dmesg 命令查看系统调用的结果:
可见输出 "20192121026_邓智超",说明添加系统调用成功
# 进程通信# 代码实践 1# 信号 - SIGNAL创建 signal.c 文件,并在其中添加以下代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <signal.h> int k;void int_func (int sig) 0 ;printf ("int_func\n" );int main () 1 ;while (k == 1 )printf ("Hello!\n" );printf ("OK!\n" );exit (0 );
通过 gcc signal.c 和 **./a.out** 命令运行得到以下结果:
# 管道 - PIPE创建 pipe.c 文件,并在其中添加以下代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main () int p1,fd[2 ];char outpipe[50 ];char inpipe[50 ];while ((p1 = fork()) == -1 );if (p1 == 0 )strcpy (inpipe, "This is a message!" );1 ], inpipe, 50 );exit (0 );else 0 );0 ], outpipe, 50 );printf ("%s\n" ,outpipe);exit (0 );
通过 gcc pipe.c 和 **./a.out** 命令运行得到以下结果:
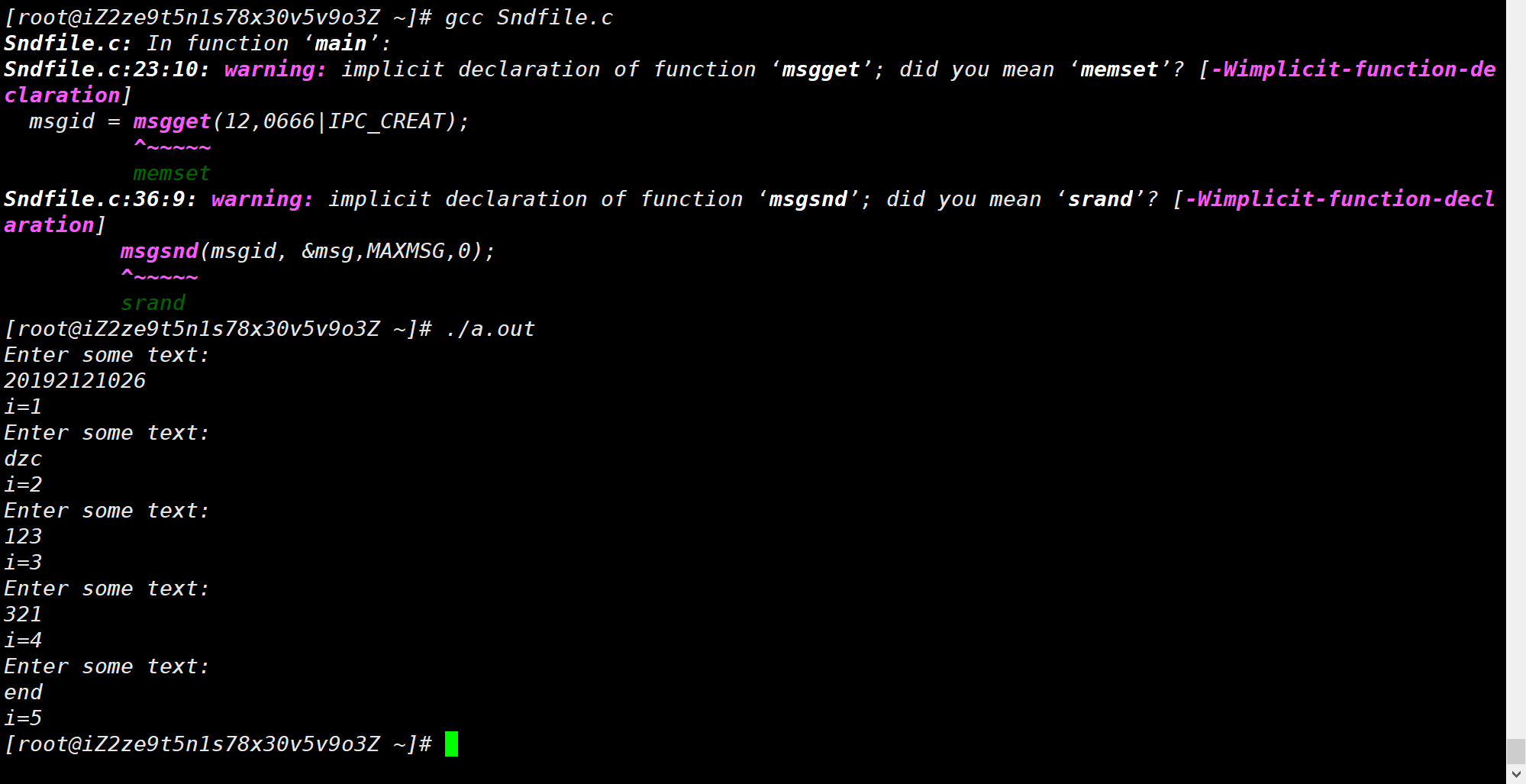
# 消息传递创建 Sndfile.c 文件,并在其中添加以下代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <linux/msg.h> #define MAXMSG 512 struct my_msg { long int my_msg_type;int i;char some_text[MAXMSG];int main () int msgid;char buffer[BUFSIZ];12 ,0666 |IPC_CREAT);while (1 )puts ( "Enter some text:" );stdin );printf ("i=%d\n" , msg.i);3 ;strcpy (msg.some_text,buffer); 0 );if (strncmp (msg.some_text, "end" ,3 )==0 )break ;exit (0 );
通过 gcc Sndfile.c 和 **./a.out** 命令运行得到以下结果:
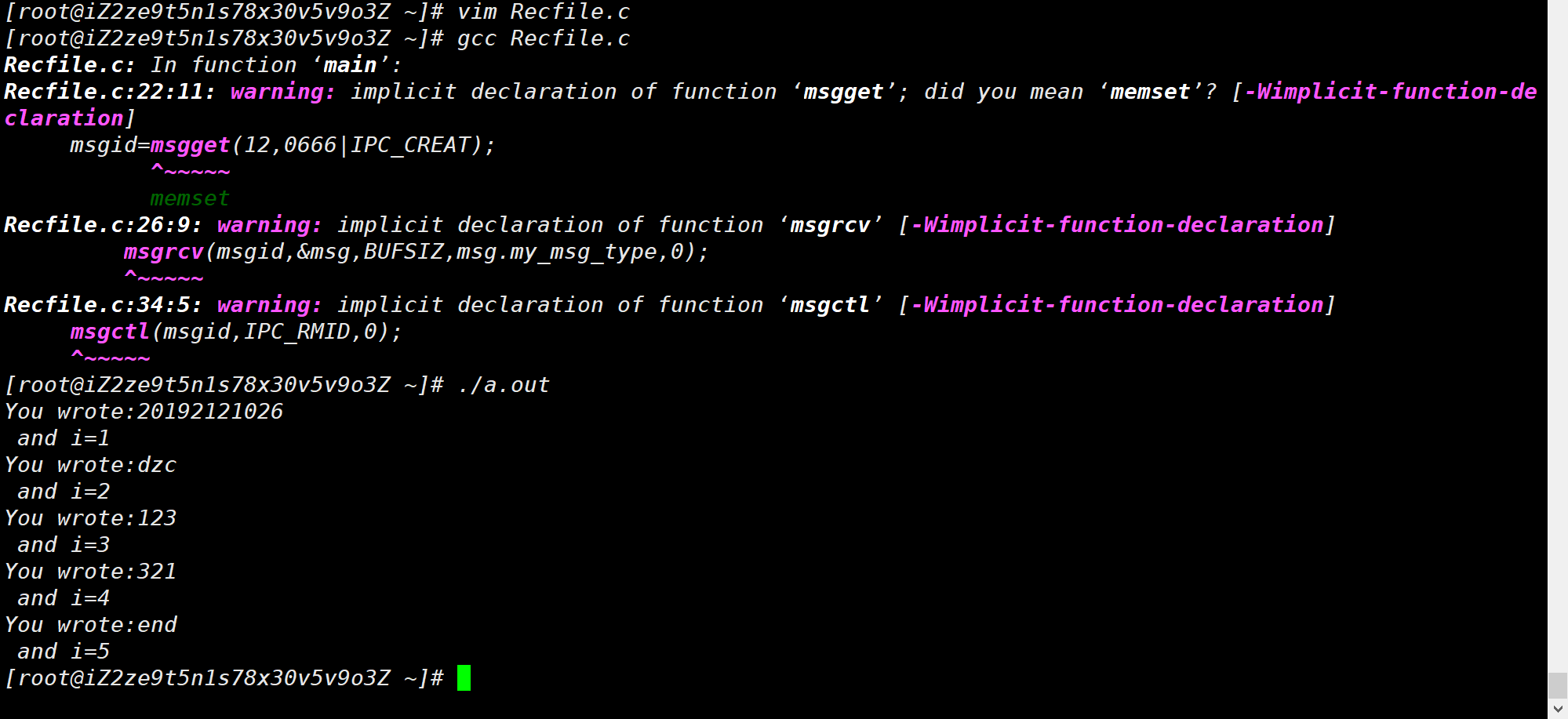
创建 Recfile.c 文件,并在其中添加以下代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <linux/msg.h> #define MAXMSG 512 struct my_msg { long int my_msg_type;int i;char some_text[MAXMSG];int main () int msgid;3 ;12 ,0666 |IPC_CREAT);while (1 )0 );printf ("You wrote:%s and i=%d\n" ,msg.some_text,msg.i);if (strncmp (msg.some_text, "end" ,3 )==0 )break ;0 );exit (0 );
通过 gcc Recfile.c 和 **./a.out** 命令运行得到以下结果:
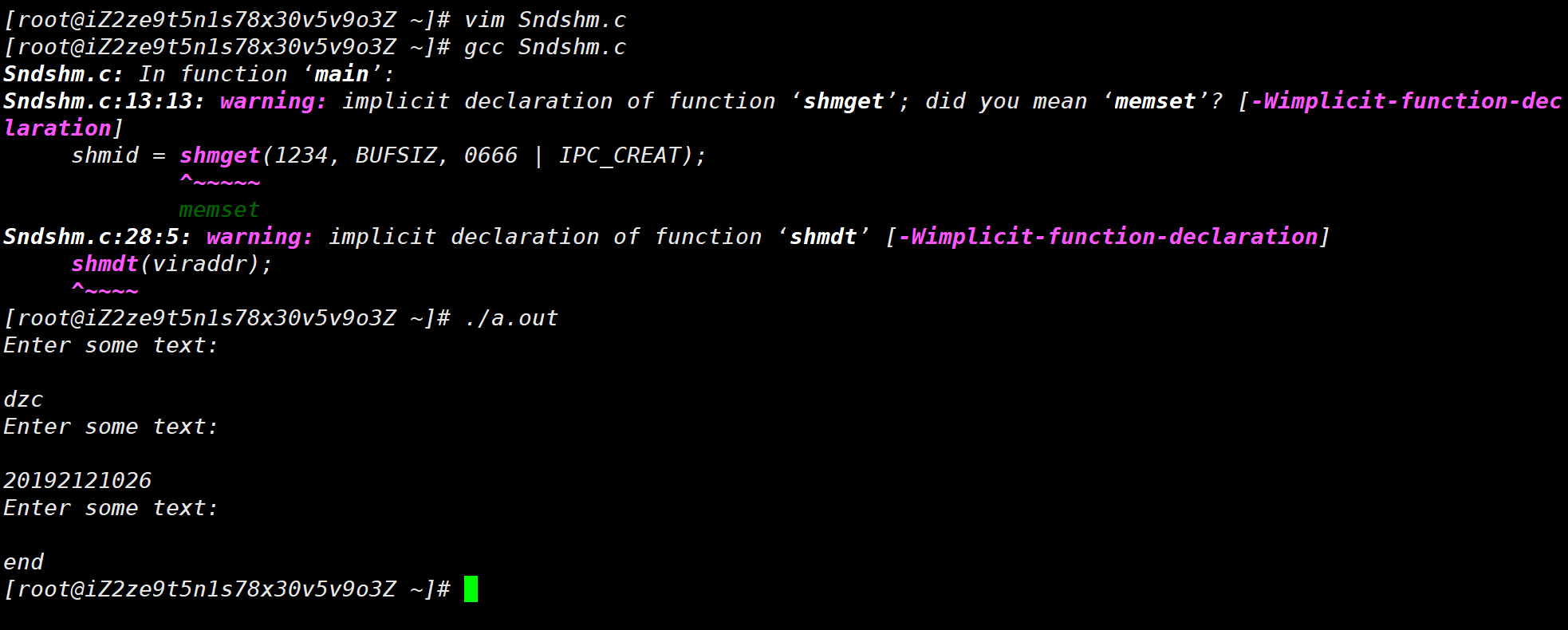
# 共享内存创建 Sndshm.c 文件,并在其中添加以下代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <linux/shm.h> int main () int shmid;char *viraddr;char buffer[BUFSIZ];1234 , BUFSIZ, 0666 | IPC_CREAT);char *)shmat(shmid, 0 , 0 );while (1 )puts ("Enter some text:\n" );stdin );strcat (viraddr, buffer);if (strncmp (buffer, "end" , 3 ) == 0 )break ;exit (0 );
通过 gcc Sndshm.c 和 **./a.out** 命令运行得到以下结果:
创建 Revshm.c 文件,并在其中添加以下代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/shm.h> int main () int shmid;char *viraddr;1234 , BUFSIZ, 0666 | IPC_CREAT);char *)shmat(shmid, 0 , 0 );printf ("Your message is :\n%s" , viraddr);0 );exit (0 );
通过 gcc Revshm.c 和 **./a.out** 命令运行得到以下结果:
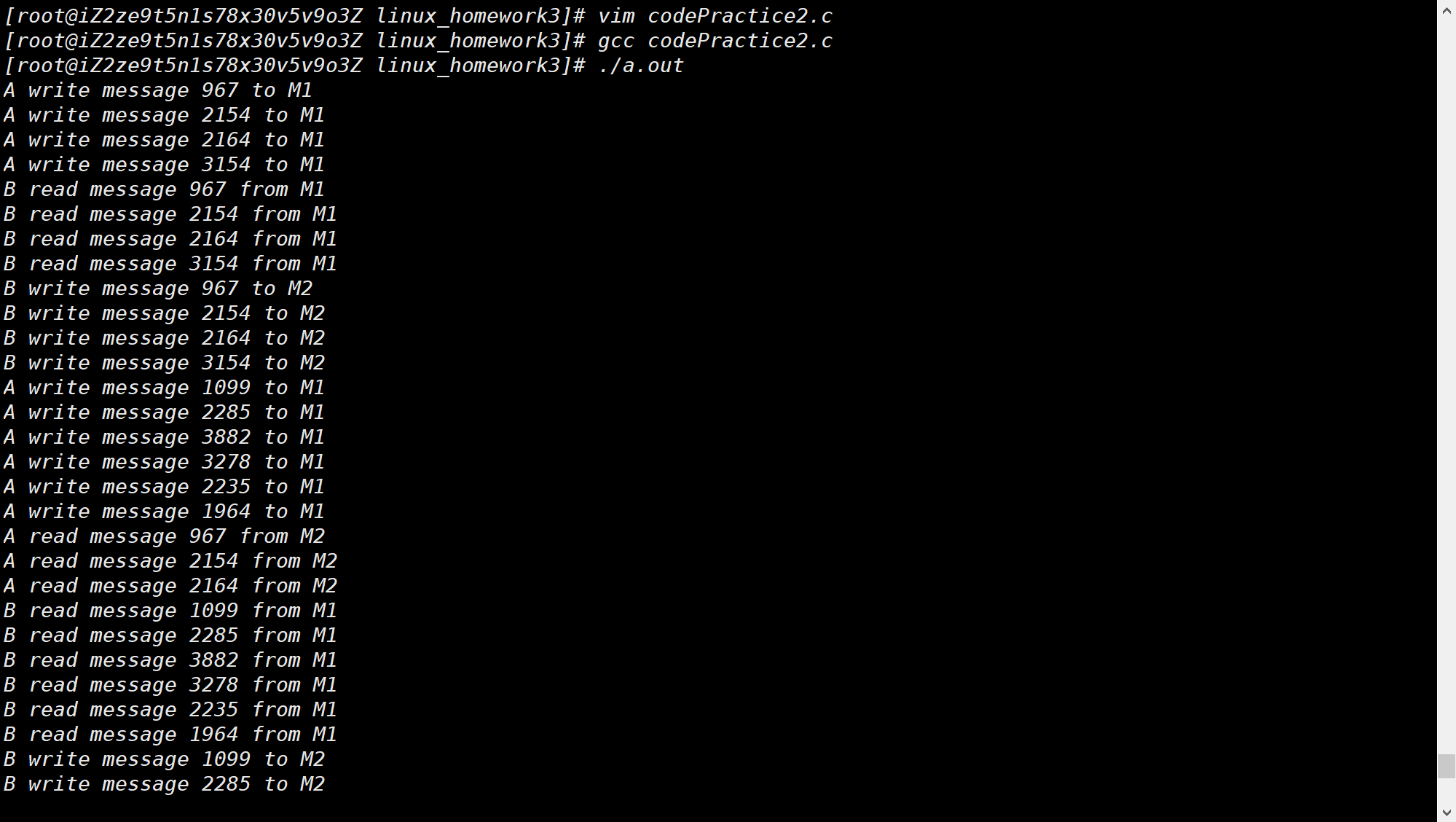
# 代码实践 2# 思路
为 M1,M2 分别建立两个共享空间,创建三个进程,父进程,A 进程,B 进程,将共享内存连接到当前进程的地址空间,使得三个进程都能访问 M1,M2。
设置两个信号量 A_ENABLE,B_ENABLE ,分别表示允许 A 执行和允许 B 执行。程序开始的时候,A_ENABLE = 1,B_ENABLE = 0。每次 A 执行时,对 A_ENABLE 执行 P 操作 ,A 结束时,对 B_ENABLE 执行 V 操作 ;每次 B 执行时,对 B_ENABLE 执行 P 操作 ,B 结束时,对 A_ENABLE 执行 V 操作 ,这样就可以达到 A 和 B 轮流执行的效果。
为了使程序能够有较好的效果且能够停止,这里设置 A 和 B 分别执行 4 次 操作
此代码参考生产者消费者问题 多进程共享内存 - LightningStar - 博客园 (cnblogs.com) 并按照题目要求做了修改以符合作业要求
# 代码1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/shm.h> #include <time.h> #include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/sem.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #define MAX_NUM 4096 struct Resource { int message[MAX_NUM];int front;int rear;struct Resource M [2];union semun { int value;enum MUTEX { int semid;int shmid[2 ];struct Resource *shm [2];void attach_shm () 0 ] = (struct Resource *)shmat(shmid[0 ], NULL , 0 );1 ] = (struct Resource *)shmat(shmid[1 ], NULL , 0 );if (shm[0 ] == (struct Resource *)-1 || shm[1 ] == (struct Resource *)-1 )fprintf (stderr , "shmat failed\n" );exit (EXIT_FAILURE);void detach_shm () if (shmdt((void *)shm[0 ]) == -1 || shmdt((void *)shm[1 ]) == -1 )fprintf (stderr , "shmdt failed\n" );exit (EXIT_FAILURE);void P (short unsigned int num) struct sembuf sb =-1 , 0 1 );void V (short unsigned int num) struct sembuf sb =1 , 0 1 );int readMessage (int id) int message = 0 ;1 ]->message[shm[-id + 1 ]->front];1 ]->front = (shm[-id + 1 ]->front + 1 ) % MAX_NUM;return message;int writeMessage (int id) int message = rand() % 4096 + 1 ;1 ) % MAX_NUM;return message;void processA () for (int m = 0 ; m < 4 ; m++)int ele1Number = (shm[0 ]->rear - shm[0 ]->front + MAX_NUM) % MAX_NUM;int maxNum = MAX_NUM - ele1Number;int randInt = rand() % 10 + 1 ;int times = maxNum < randInt ? maxNum : randInt;for (int i = 0 ; i < times; i++)printf ("A write message %d to M1\n" , writeMessage(0 ));if (shm[1 ]->front != shm[1 ]->rear)int eleNumber = (shm[1 ]->rear - shm[1 ]->front + MAX_NUM) % MAX_NUM;int times = rand() % eleNumber + 1 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < times; i++)printf ("A read message %d from M2\n" , readMessage(0 ));void processB () for (int m = 0 ; m < 4 ; m++)int eleNumber = (shm[0 ]->rear - shm[0 ]->front + MAX_NUM) % MAX_NUM;int randInt = rand() % 10 + 1 ;int times = eleNumber < randInt ? eleNumber : randInt;for (int i = 0 ; i < times; i++)printf ("B read message %d from M1\n" , readMessage(1 ));for (int i = 0 ; i < times; i++)printf ("B write message %d to M2\n" , writeMessage(1 ));int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) pid_t ppid = getpid();key_t )1234 , NUM_MUX, IPC_CREAT | 0600 ); if (semid == -1 )"semget" );union semun s ;1 ;0 ;0 ] = shmget((key_t )1234 , sizeof (M[0 ]), 0666 | IPC_CREAT);1 ] = shmget((key_t )5678 , sizeof (M[1 ]), 0666 | IPC_CREAT);if (shmid[0 ] == -1 || shmid[1 ] == -1 )fprintf (stderr , "shmget failed\n" );exit (EXIT_FAILURE);for (int i = 0 ; i < 2 ; i++)memset (shm[i]->message, 0 , sizeof (shm[i]->message));0 ;0 ;pid_t child_pid[2 ];int i = 0 ;for (i = 0 ; i < 2 ; i++)if (child_pid[i] == 0 ) break ;if (i == 0 ) else if (i == 1 ) if (getpid() == ppid) for (int i = 0 ; i < 2 ; i++) NULL , 0 );if (shmctl(shmid[0 ], IPC_RMID, 0 ) == -1 || shmctl(shmid[1 ], IPC_RMID, 0 ) == -1 )fprintf (stderr , "shmctl(IPC_RMID) failed\n" );exit (EXIT_FAILURE);return 0 ;
# 运行截图